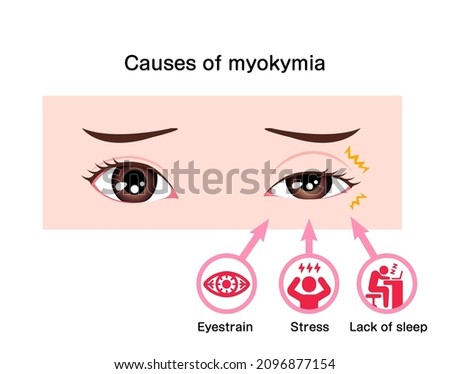
There are many different myokymia types. It’s important to understand the differences between them, because there are no known causes. The condition is characterized by an uncontrolled, slow movement of the muscles. It can be compared to a worm moving in a circular motion. It can also occur during sleep. Myokymia affects muscles on only one side of the body, or it can spread to any area of the body.
Patients with myokymia commonly experience pain, twitching, cramping, stiffness, or weakness. They may also have sensory symptoms. The first two types are characterized by pain and cramps. The last type is characterized by a lack of sensation. The pain is often accompanied by muscle weakness and twitching. In both types, treatment will focus on relieving symptoms. BOTOX injections are another common form of myokymia.
Myokymia with eyelids is the most common type. This condition is associated with inflammation leading to demyelination of the eyelid muscle. The disease can also be caused by tumors or damage in brainstem areas. Radiation therapy can exacerbate the condition. The best treatment is to treat the underlying condition. For eyelid myokymia, there are several options for treatment.
Some people who have myokymia have eyelid twitching without an upper eyelid droop. This type of myokymia may not be noticeable to an observer. However, if the twitching is severe enough, the upper lid will usually droop. There are also some conditions in which the eyes close for no reason at all. There is no known cure for myokymia.
There are many different myokymia types, and each has its own unique set of symptoms. Some are more severe than others, but all are common and need to be evaluated to determine if you’re suffering from one of these conditions. Generally, they all share the same symptoms: intense muscle contraction, eyelid trembling, and a shaky or tilted vision. Sometimes, myokymia may occur intermittently, disappear, or change in severity.
There are two main subtypes of myokymia. The most common type is facial myokymia, which is caused by inflammation causing demyelination. Other types can be triggered by tumors in the face, hemifacial spasm, or ocular neuromyotonia. Some patients may also have a history of radiation therapy. In these cases, the affected nerves are damaged, and they may not be responding to chemotherapy.
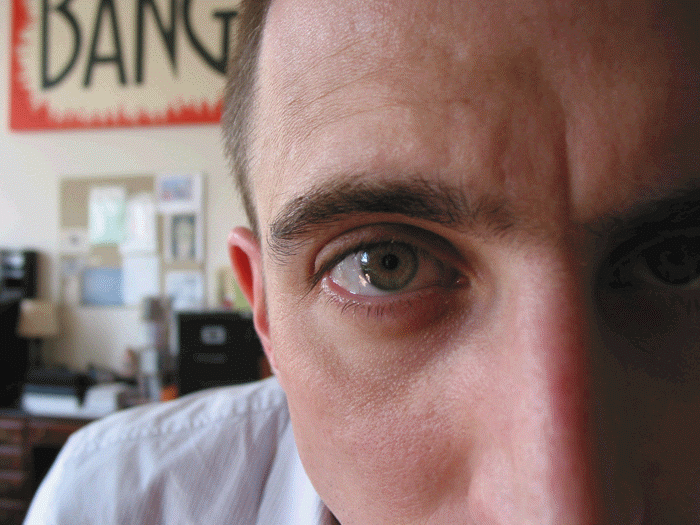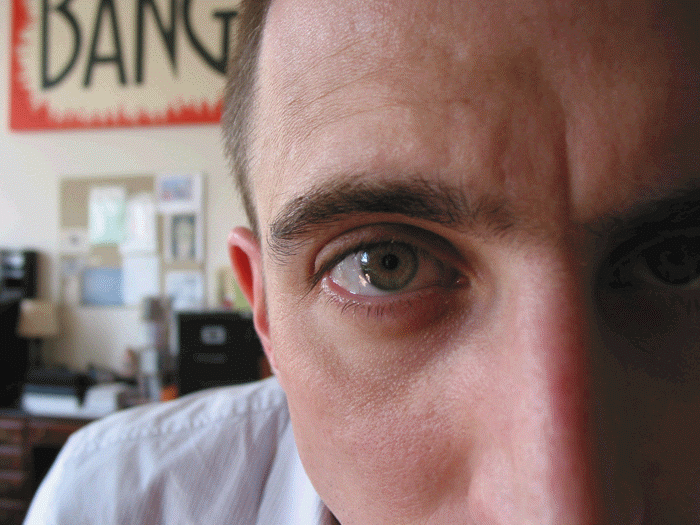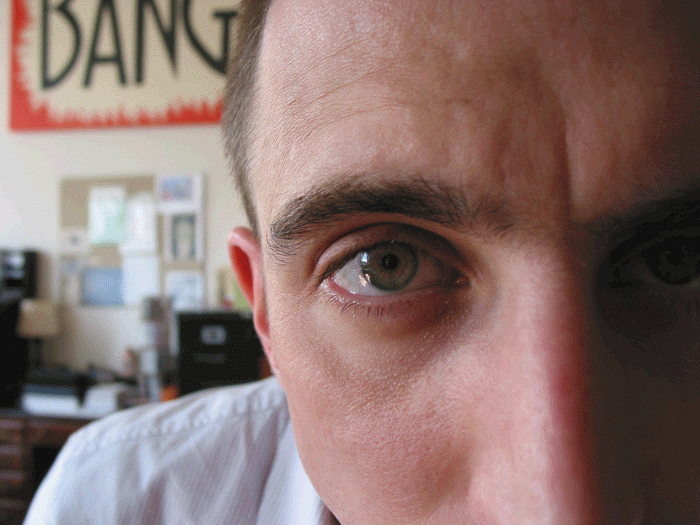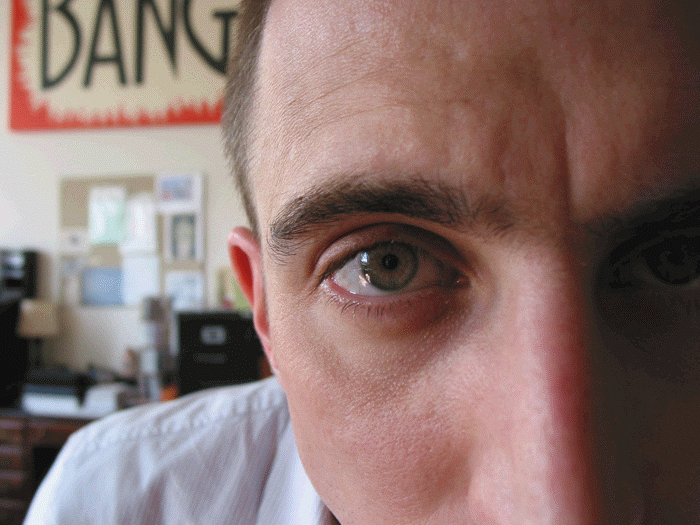
There are two types of myokymia: the most common type is eyelid myokymia. It occurs when the facial nerve nucleus is damaged. Symptoms of eyelid myokymia include twitching of the eyelids. Some people may not experience pain. Other people may experience mild nystagmus-like movements in their eye. A doctor will examine the affected eye to rule out systemic disease.
Symptoms of myokymia may include pain, spasms, weakness, and twitching of the eyelid muscles. Other symptoms can include drooping of the upper eyelids and facial nerves. Surgical procedures can correct myokymia by removing the affected muscle. In some cases, patients can live with myokymia for years.
In other types of myokymia, muscle twitches may be present with no visible result to the observer. Eyelid myokymia symptoms can be intermittent or constant, and they can affect the muscles of the face and eyes. There are two types of myokymia: the first is a condition of the eyelids. Despite its name, myokymia is a type of disorder of the nerves located in the face and muscles of the body.
Eyelid myokymia is characterized by intermittent and repetitive small contractions of the eyelids. These symptoms are most common in people with eyelid disease. Some people experience these symptoms every day, but they can be prevented with the right treatment. If you have any of these symptoms, you should see your doctor as soon as possible and get more information about symptoms and disease prevention at https://www.motherandcare.in.th/. In some cases, eyelid twitches can be caused by stress or exposure to a substance.
Facial myokymia is a disease of the eyelids. This may affect the upper or lower eyelids. In most cases, this occurs in the lower eyelid. The symptoms are similar to those of blepharospasm but can become chronic. There are also some forms of myokymia that affect the heart, including eye myokymia.